ML-LAB-VI-SEM
Exercise 09
Building an Artificial Neural Network (ANN) using Backpropagation
Aim
To build a basic Artificial Neural Network (ANN) and implement the Backpropagation algorithm for training using Python.
Procedure/Program
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# sigmoid activation function
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
# derivative of sigmoid function
def sigmoid_derivative(x):
return x * (1 - x)
# training dataset: Logical XOR Problem
X = np.array([
[0, 0],
[0, 1],
[1, 0],
[1, 1]])
y = np.array([[0], [1], [1], [0]])
# initialize neural network parameters
input_layer_neurons = X.shape[1] # 2 features (X1 and X2)
hidden_layer_neurons = 4 # Number of neurons in the hidden layer
output_layer_neurons = 1 # Output layer (binary classification)
# initialize weights and biases
np.random.seed(42)
hidden_weights = np.random.rand(input_layer_neurons, hidden_layer_neurons)
hidden_bias = np.random.rand(1, hidden_layer_neurons)
output_weights = np.random.rand(hidden_layer_neurons, output_layer_neurons)
output_bias = np.random.rand(1, output_layer_neurons)
# learning rate
learning_rate = 0.1
epochs = 10000
# list to store error history for plotting
error_history = []
# training the ANN using Backpropagation
for epoch in range(epochs):
# forward Propagation
hidden_layer_input = np.dot(X, hidden_weights) + hidden_bias
hidden_layer_output = sigmoid(hidden_layer_input)
output_layer_input = np.dot(hidden_layer_output, output_weights) + output_bias
predicted_output = sigmoid(output_layer_input)
# backpropagation (Error Calculation)
error = y - predicted_output
d_predicted_output = error * sigmoid_derivative(predicted_output)
# error at Hidden Layer
error_hidden_layer = d_predicted_output.dot(output_weights.T)
d_hidden_layer = error_hidden_layer * sigmoid_derivative(hidden_layer_output)
# update weights and biases using Gradient Descent
output_weights += hidden_layer_output.T.dot(d_predicted_output) * learning_rate
output_bias += np.sum(d_predicted_output, axis=0, keepdims=True) * learning_rate
hidden_weights += X.T.dot(d_hidden_layer) * learning_rate
hidden_bias += np.sum(d_hidden_layer, axis=0, keepdims=True) * learning_rate
# append the mean error to error_history
if epoch % 1000 == 0:
error_history.append(np.mean(np.abs(error)))
print(f"Epoch {epoch} | Error: {np.mean(np.abs(error))}")
# final predictions after training
print("\nFinal Predicted Output:")
print(predicted_output)
# plotting the error curve
plt.plot(range(0, epochs, 1000), error_history) # only plot every 1000th epoch
plt.xlabel("Epochs")
plt.ylabel("Mean Absolute Error")
plt.title("Error Curve during Backpropagation Training")
plt.show()
Output/Explanation
-
Output:
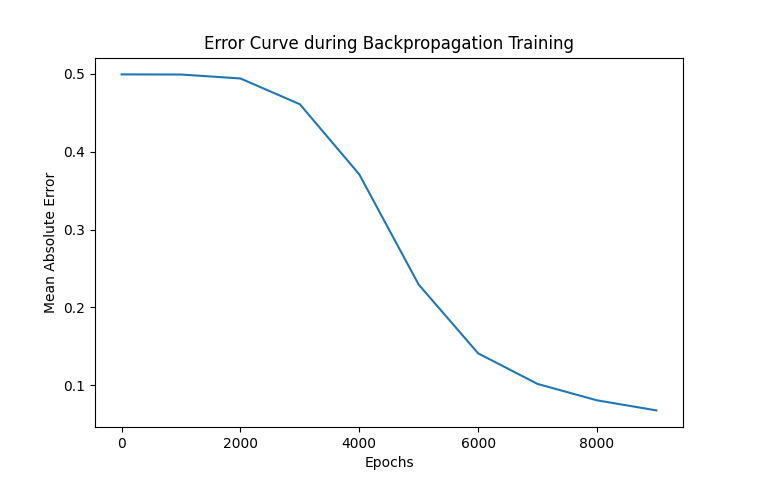
Epoch 0 | Error: 0.49914791405546904 Epoch 1000 | Error: 0.4989908274224632 Epoch 2000 | Error: 0.4939211220442684 Epoch 3000 | Error: 0.46086324847622706 Epoch 4000 | Error: 0.3708114875497051 Epoch 5000 | Error: 0.22936859341508167 Epoch 6000 | Error: 0.14117007926640446 Epoch 7000 | Error: 0.10187019467760633 Epoch 8000 | Error: 0.08085064924133498 Epoch 9000 | Error: 0.067907182961121 Final Predicted Output: [[0.04690963] [0.95663392] [0.92548675] [0.07177571]]The program builds an Artificial Neural Network (ANN) with 2 input neurons, 1 hidden layer with 4 neurons, and 1 output neuron. The Backpropagation algorithm is used to update weights and biases during training.
- Epoch-wise error: The error (mean absolute error) for every 1000 epochs is printed during training.
- Final Predicted Output: After training is complete, the predicted output for the XOR problem is displayed.
- Error Curve: A plot is generated showing the error reduction during training.
-
Explanation:
- The training dataset used here is the XOR problem, where the inputs
Xare 2 binary variables, and the outputyis the XOR of those inputs. - Sigmoid activation function is used for both the hidden and output layers.
- The forward propagation step calculates the outputs of the hidden and output layers.
- The backpropagation step calculates the error between the predicted output and the actual output, and adjusts the weights using the gradient descent algorithm.
- The weights and biases are updated in each epoch to minimize the error.
- The error curve shows the decrease in error as the network learns to predict the output accurately.
- The training dataset used here is the XOR problem, where the inputs
This program illustrates how to implement a simple neural network with backpropagation for binary classification tasks (such as XOR). The network learns over multiple epochs and minimizes error using the Gradient Descent technique.