OOAD-LAB-VI-SEM
Exercise 04
Drawing Class Diagram and Use Case Diagram of Railway Reservation System
Aim
To draw the Class Diagram and Use Case Diagram for a Railway Reservation System.
Theory
-
Class Diagram: A class diagram is a static structure diagram in UML that shows the system’s classes, their attributes, methods, and relationships. It is used to model the system’s internal structure.
-
Use Case Diagram: A use case diagram captures the functional requirements of a system by depicting the interactions between users (actors) and the system, represented as use cases.
For a Railway Reservation System, the class diagram will represent entities like Train, Reservation, Passenger, Payment, and Ticket. The use case diagram will depict interactions such as searching for trains, booking tickets, and making payments.
Procedure/Program
- Class Diagram:
- Identify the main components of the Railway Reservation System:
Train: Attributes liketrainID,trainName,source,destination,departureTime,availableSeats.Reservation: Attributes likereservationID,passenger,train,reservationDate,status.Passenger: Attributes likepassengerID,name,email,phone,address.Ticket: Attributes liketicketID,reservation,seatNumber,ticketType,price.Payment: Attributes likepaymentID,paymentDate,amount,paymentMethod,status.
- Define relationships:
- Association between
TrainandReservation(a train can have multiple reservations). - Association between
ReservationandPassenger(a reservation is linked to a passenger). - Association between
ReservationandTicket(a reservation can have one or more tickets). - Association between
PaymentandReservation(payment is linked to a reservation).
- Association between
- Specify operations (methods):
Train: Methods likecheckAvailability(),updateSchedule(),viewTrainDetails().Passenger: Methods likecreateAccount(),searchTrains(),viewReservationHistory().Reservation: Methods likecreateReservation(),cancelReservation(),viewReservationDetails().Ticket: Methods likegenerateTicket(),checkTicketStatus(),updateTicketDetails().Payment: Methods likeprocessPayment(),generateInvoice(),verifyPayment().
- Identify the main components of the Railway Reservation System:
- Use Case Diagram:
- Identify actors in the system:
Passenger: The primary user who searches for trains, makes reservations, and processes payments.Admin: The user who manages the trains, schedules, and reservations.
- Identify use cases:
- For
Passenger:Search Trains,Book Ticket,Make Payment,Cancel Reservation,View Reservation Details. - For
Admin:Add Train,Modify Train Schedule,View Reservations,Manage Payments.
- For
- Draw the system boundary:
- Draw a rectangle to represent the system’s boundary and place the use cases inside it.
- Connect the actors (
Passenger,Admin) to the use cases they interact with. - Use relationships such as
includeorextendfor actions that depend on others. For example,Book Ticketmay includeMake Payment.
- Identify actors in the system:
Output/Explanation
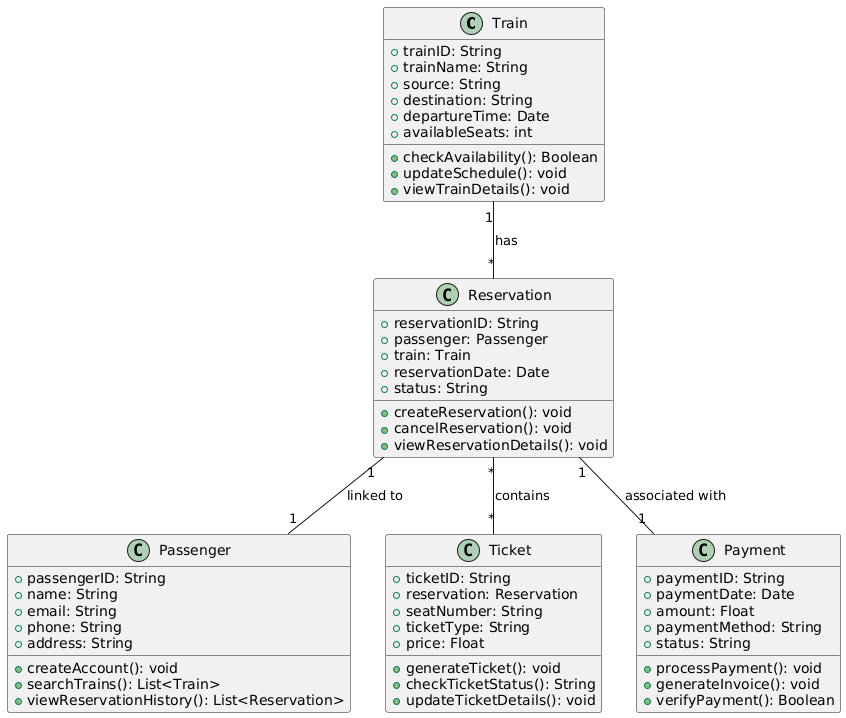
- Class Diagram:
- The output will be a class diagram illustrating the system’s classes, attributes, methods, and the relationships between entities like
Train,Reservation,Passenger,Ticket, andPayment.
- The output will be a class diagram illustrating the system’s classes, attributes, methods, and the relationships between entities like

- Use Case Diagram:
- The output will be a use case diagram showing how the
PassengerandAdminactors interact with the system through use cases like searching trains, booking tickets, and managing payments.
- The output will be a use case diagram showing how the
Explanation:
-
The Class Diagram provides a detailed structural view of the Railway Reservation System, showing how different entities relate to each other, which helps in understanding the internal working of the system.
-
The Use Case Diagram represents a high-level view of the system’s functionalities from the user’s perspective, capturing the interactions between users and the system’s features.